[Article here.]
It is often said that looking through a telescope is like peering back in time, because of the millions of years it takes light from distant cosmic objects to reach Earth. Now scientists have calculated that they may be able to see far enough back to observe the birth of the very first stars – with the first images possibly available as early as next year. They have also pinpointed when this momentous event occurred.
Observing the moment when the universe was first bathed in light, the cosmic dawn, is a major quest in astronomy.
“All of the chemical elements that make up you and me are synthesised in stars, so in some sense, cosmic dawn is our own birth,” said Prof Richard Ellis at University College London, who was involved in the research. “It has been a holy grail for astronomers to not only predict when this occurred, but to actually witness it.”
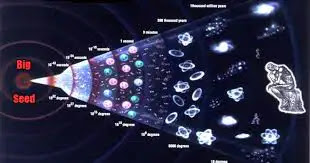
The universe is thought to have started with the big bang seed 13.8bn years ago, but for the first few hundred million years it was a dark and starless expanse of hydrogen gas awash with radiation, known as the cosmic microwave background. Gradually, those clouds of hydrogen gas began to clump together under aggregate due to gravity and to heat up, until they eventually reached temperatures equivalent to the centre of the sun, where nuclear fusion could occur. This is how the first stars were born.
Directly witnessing the event is beyond the range of our current telescopes, but it could be possible with the launch of the James Webb space telescope, scheduled for November. “We predict from our measurements that it will have the sensitivity to witness this cosmic dawn, maybe as early as next year,” Ellis said.
However, to achieve this astronomers first need to know where to look. Ellis, together with an international team of researchers, used images from the Hubble and Spitzer telescopes to examine six of the most distant galaxies known, whose light has taken most of the universe’s lifetime to reach us.
Doing so meant pushing the capabilities of these telescopes to their limits, but by combining these images with spectroscopic measurements from powerful ground-based telescopes – the Atacama Large Millimetre Array (ALMA) and the European Very Large telescope in Chile, and the Gemini South and twin Keck telescopes in Hawaii – they calculated that the distance of these galaxies away from Earth corresponded to a “look back” time of more than 13bn years ago, when the universe was only 550m years old.
The research, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, also suggests the “switching on” of these first stars was a gradual process, rather than a single coordinated explosion of light.
“We found that the ages of the six galaxies we looked at were slightly different, so they didn’t all switch on at once,” said Ellis. “We now eagerly await the launch of the James Webb space telescope. It has got seven times the light-gathering power of Hubble and extends further into the infrared, which is crucial for going back further in time.”
The Nasa-led telescope is the successor to the Hubble observatory, comprising an infrared observatory, an immense mirror 6.5 metres wide, and a diamond-shaped sunshield. Assuming its launch goes to plan, it will become the premier space observatory over the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide.
Yet it is a high-risk mission, because the telescope’s mirror and solar panels must unfold in space and it is being sent into a solar orbit beyond the moon, meaning there is little prospect of repairing it if something goes wrong. “Our hearts will be in our mouths when the James Webb goes up, because everything has to work,” Ellis said.
We may also need to temper our expectations of what the cosmic dawn will look like, assuming the telescope can directly observe it. “If you were there, there would be lots of little stars switching on. And over a period of 100m years, many more of them would switch on, so it would be a dramatic event,” Ellis said. “The trouble is, with a telescope you will just see a handful of objects that could be candidates for cosmic dawn, and then we will have to look at them in detail, and see whether they are free from the heavy chemical elements, which would be consistent with a first generation star.”
Cinematically then, it may be an anticlimax. But as a scientific achievement, it could be momentous.